1. Shikantaza as the essential doctrine of Soto Zen Buddhism In the Sotoshu Constitution (Sotoshu Shuken), Soto Zen Buddhist doctrine (Shushi) is set down as “. . . abiding …
Half a century passed since Bodhidhama of Modern Times or Master Taisen Deshimaru brought the Zen practice to Europe. He opened a new chapter in Europe’s spiritual environment, by …
The Five Precepts – termed as pancasila in Pali, constitute the basic ethical guidelines taught by the Buddha for lay practitioners. They are known as the “basic” precepts as …
If we know what to look for, we can tell the meaning of a Buddha Statue by looking at the pose / posture, and the accompanying hand gestures, called …
AUM or OM (in Devanagari ॐ) is one of the most sacred symbols in Hinduism. In Sanskrit known as praṇava (प्रणव) lit. “to sound out loudly” or oṃkāra (ओंकार) lit. “oṃ syllable”) Hindus consider AUM …
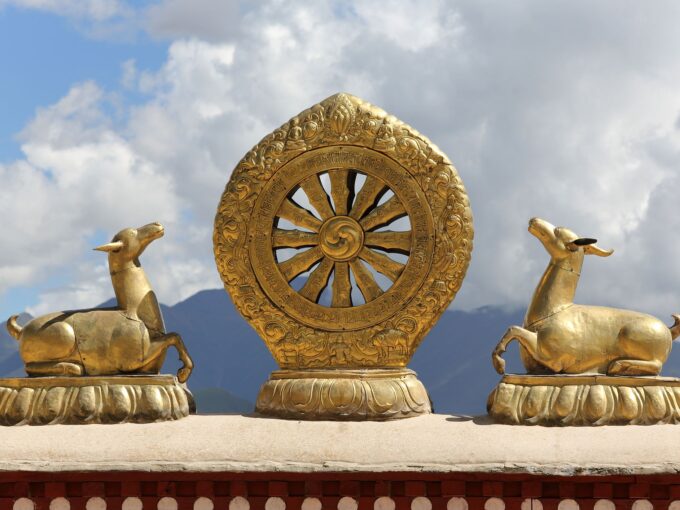
Cakkavattisihanāda Sutta is also known as The Discourse on the Lion-roar of the Wheel-turner. This Sutra is an important early discourse (number 26 in the Dīgha Nikāya) and it …
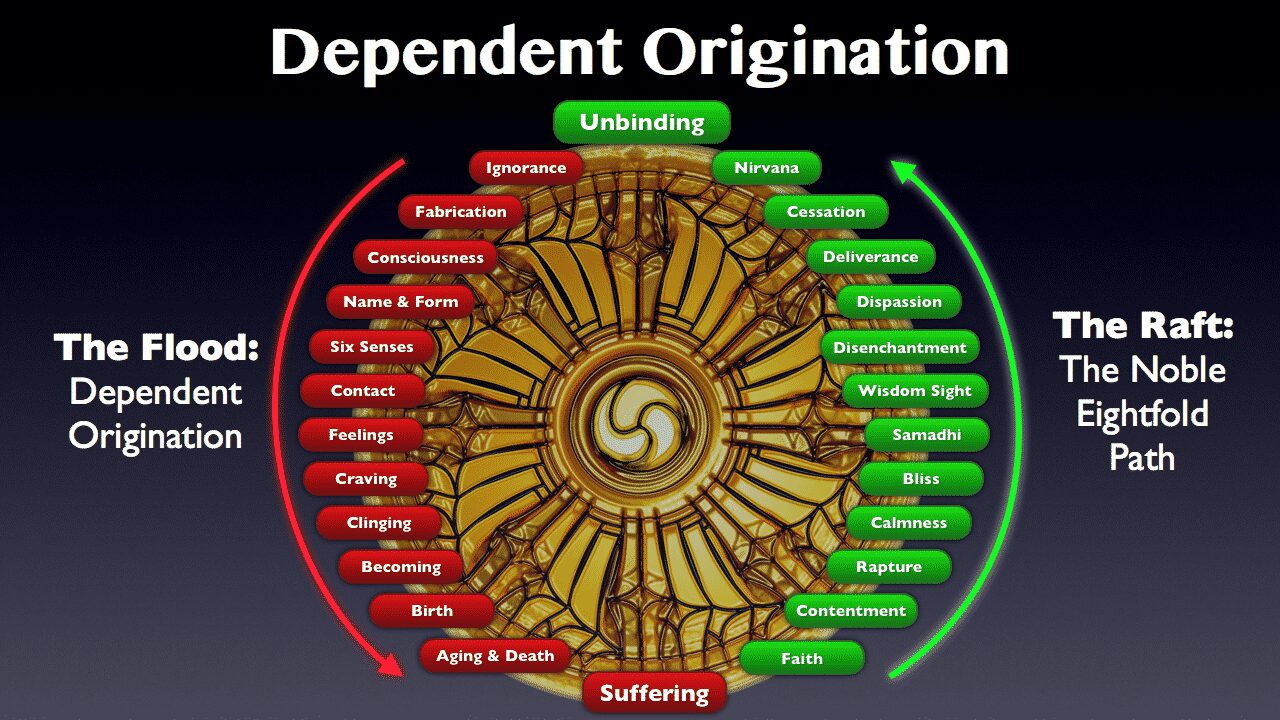
The principle of dependent origination— paṭicca-samuppāda — is a defining characteristic of Buddhist philosophy. Paṭicca-samuppāda explains the core statement of the Buddha, that the causes of sorrow and the causes …
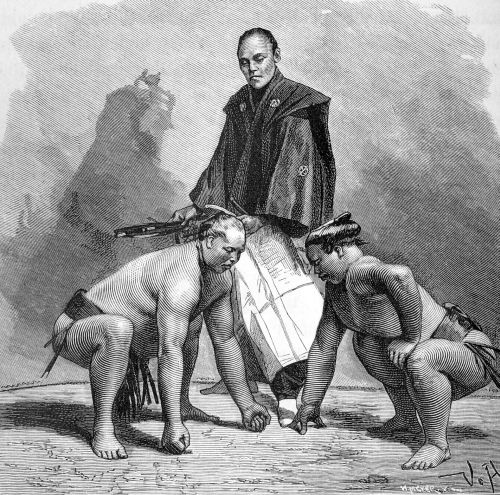
In the early days of the Meiji era there lived a well-known wrestler called O-nami, Great Waves. O-nami was immensely strong and knew the art of wrestling. In his …
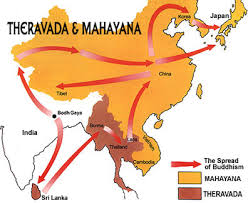
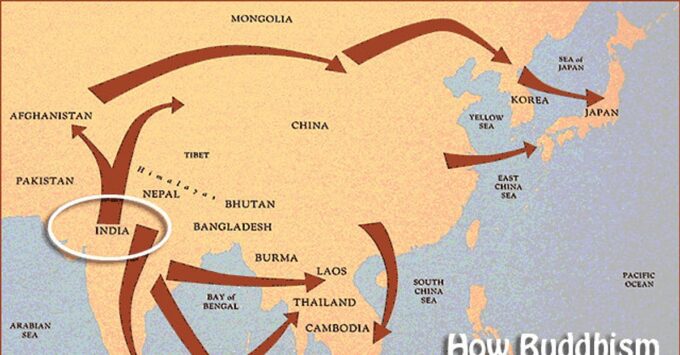
Buddhism is one of the oldest religions of the world. Buddhism is practiced by a large number of people in many parts of the world, particularly in the South …
Dzogchen is an ancient spiritual teaching developed in Tibet within the Tibetan Buddhist tradition. It does not belong to a school or religious system. Dzogchen is a set of …